Who does not know this situation. One returns to the phone and recognizes a missed call. Then one usually wants to know who the caller is, but the phone only displays an unknown phone number. Usually the next step is to google the number or use a reverse number search to see who called, or at least from where the call came. This article is about improving this situation using Nokia´s smartphone N900 .
Concept
Basically there are two applications for the N900 phone which can be used to improve the above scenario. These are callerid and extcalllog. The callerid application displays the details for the phone number of an incoming call. This is done by automatically accessing a reverse number search engine. If the number is not available in the database, which happens quite often due to privacy reasons, it compares the area code with a local database and displays at least the region, the call comes from. The extcalllog application displays the call history just as the phone application of the N900 does, but it has got two major advantages. First it is not restricted to the last 30 days as the N900s phone application is, second it is open source, thus it can be extended. This makes it possible to combine the functionality of extcalllog and callerid.
Prerequirements
As a prerequirement it is necessary to install and configure the callerid application for the users region. It is available from the extras-devel repository. Configuration is done by supplying an xml file describing the reverse search. This file has to be placed in /opt/callerid/ and named correctly. For example the xml file for the german reverse number search must have the filename de.xml. The contents of the file, taken from [1] are being shown below.
<config>
<directory>
<query>http://www.klicktel.de/inverssuche/index/search?method=searchSimple&_dvform_posted=1&phoneNumber=</query>
<name>
<find class="namelink"/>
</name>
<address>
<find class="data track"/>
</address>
</directory>
</config>For displaying the area code in case of a failed reverse lookup a local database file has to be placed in /opt /callerid/. For Germany this file must be named de.txt. It can be created from the official list of area codes, ONB, provided by the Bundesnetzagentur. For convenience you can download the file in proper format for callerid from here: de.txt.zip (1283 downloads ) . Copy it to your device and as root user extract it to /opt/callerid. Afterwards the device signals incoming calls with a notification containing the callers name and address or at least, if these are not available, the callers city.
Modifications
The next step is to extend the user interface to display the details for an incoming call. Since the default N900 phone application is not open source, the extcallog application is the only application which is extensible for this purpose. It also is available from the extras-devel repository. For the new functionallity an additional button has to be added to the user interface, which calls the callerid application with the phone number for the log entry. For this the extcalllog applications source has to be extended using my patch. You may download the patch from here: extcalllog-0.6-callerid.patch (1254 downloads ) . For convenience a binary with the patched version can be downloaded from here: extcalllog_0.6-callerid_armel.deb (1274 downloads ) . Download the binary to the device and install it with, dpkg -i extcalllog_0.6-callerid_armel.deb as root user. Or open the download in the phones browser and install it using the hildon application manager.
Usage
After installing the modified extcalllog application, it can be used as shown in figures 1 to 4. The figures show screenshots of the extcalllog application.
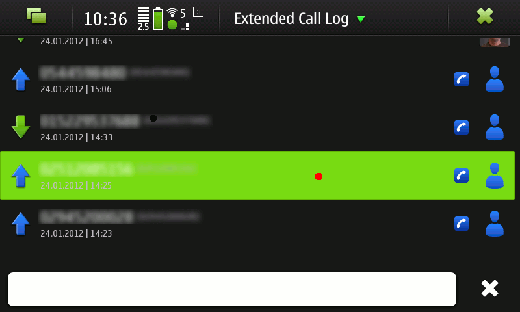
Figure 1: Selection of an entry in the callerid application
After tapping onto one entry of the call list (marked in red) the details page of the call is being opened. Figure 2 shows this page.
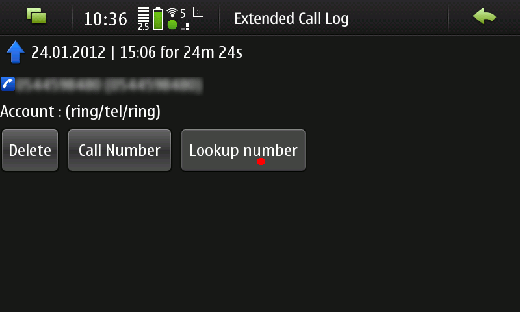
Figure2: Details page of a call with the “Lookup Number” button
The details page looks like the original one of the extcalllog application, but has got one more button, the “Lookup Number” button (also marked with a red point). After tapping onto the “Lookup Number” button the callerid application gets called for the callers number and displays the notification containing the callers details shown in Figure 3. (callers details are indecipherable in the screenshot, due to privacy reasons)
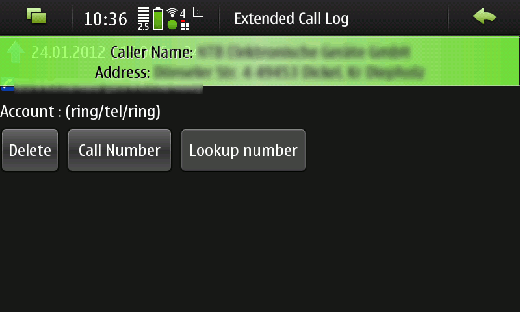
Figure 3: Notification with callers details
If the callers details are not available using the reverse number search, then only a notification displaying the callers town, like in figure 4, is being shown.
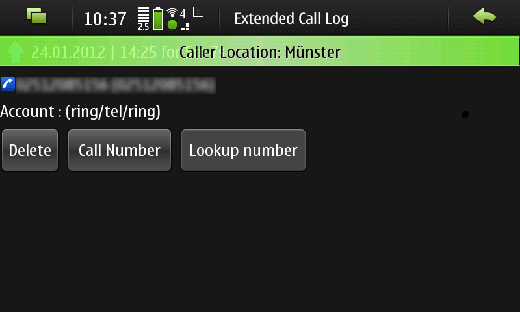
Figure 4: Notification containing callers town only
Now the N900 user is able to find out who the unknown caller is, or at least he can find out in which area he lives.
Jürgen
References:
[1] http://talk.maemo.org/showthread.php?t=70738
[2] http://talk.maemo.org/showthread.php?t=42700

Loading...
Posted in linux, maemo, maemo5, tools | 1 Comment »
 MyGNU.de
MyGNU.de







![Validate my RSS feed [Valid RSS]](https://validator.w3.org/feed/images/valid-rss.png)

